Create a simple compiler in javascript
Compilers are a very interesting topic. They are used in many different areas, from programming languages to compilers for other languages. In this post we will create a compiler that will take a simple arithmetic expression and convert it into a javascript program that will evaluate the expression.
(add 2 (subtract 4 2))
And generate this output:
add(2, subtract(4, 2));
Note: This post assumes that you have a basic understanding of javascript.
The Steps
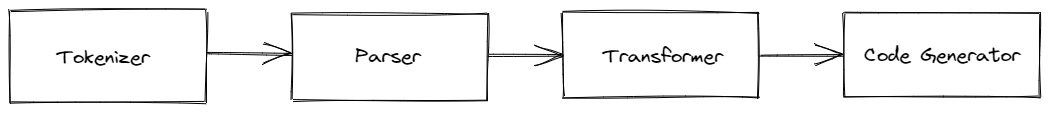
Our compiler will have 4 main parts:
- Tokenizer: This will take the input string and will split it into tokens.
- Parser: This will take the tokens and will generate an AST (Abstract Syntax Tree).
- Transformer: This will take the AST and will generate a new AST.
- Code Generator: This will take the new AST and will generate the output string.
Table of contents
Lexer
We will start by creating a lexer that will take a string and return an array of tokens.
lexer.js:
function lexer(input) {
// current position in the input
let current = 0;
// array of tokens
let tokens = [];
// loop through the input
while (current < input.length) {
let char = input[current];
// if the character is a parenthesis, add it to the tokens array
if (char === "(") {
tokens.push({
type: "paren",
value: "(",
});
current++;
continue;
}
if (char === ")") {
tokens.push({
type: "paren",
value: ")",
});
current++;
continue;
}
// if the character is a space, skip it
let WHITESPACE = /\s/;
if (WHITESPACE.test(char)) {
current++;
continue;
}
// if the character is a number, add it to the tokens array and iterate through the number to get the full number value (e.g. 123) instead of just the first digit (e.g. 1)
let NUMBERS = /[0-9]/;
if (NUMBERS.test(char)) {
let value = "";
while (NUMBERS.test(char)) {
value += char;
char = input[++current];
}
tokens.push({
type: "number",
value,
});
continue;
}
let LETTERS = /[a-z]/i;
if (LETTERS.test(char)) {
let value = "";
while (LETTERS.test(char)) {
value += char;
char = input[++current];
}
tokens.push({
type: "name",
value,
});
continue;
}
if (char === '"') {
let value = "";
char = input[++current];
while (char !== '"') {
value += char;
char = input[++current];
}
char = input[++current];
tokens.push({
type: "string",
value,
});
continue;
}
if (char === "+") {
tokens.push({
type: "plus",
value: "+",
});
current++;
continue;
}
if (char === "-") {
tokens.push({
type: "minus",
value: "-",
});
current++;
continue;
}
if (char === "*") {
tokens.push({
type: "times",
value: "*",
});
current++;
continue;
}
if (char === "/") {
tokens.push({
type: "divide",
value: "/",
});
current++;
continue;
}
throw new TypeError("I dont know what this character is: " + char);
}
return tokens;
}
module.exports = lexer;
Parser
The parser is a program that takes a sequence of tokens as input, and produces a tree as output. The tree is a data structure that represents the structure of the source code. The parser is also responsible for syntax analysis, which is the process of checking the tokens for any syntax errors.
parser.js:
function parser(tokens) {
let current = 0;
// recursive function that will iterate through the tokens array and return a node
function walk() {
let token = tokens[current];
if (token.type === "number") {
current++;
return {
type: "NumberLiteral",
value: token.value,
};
}
if (token.type === "string") {
current++;
return {
type: "StringLiteral",
value: token.value,
};
}
if (token.type === "paren" && token.value === "(") {
token = tokens[++current];
let node = {
type: "CallExpression",
name: token.value,
params: [],
};
token = tokens[++current];
while (
token.type !== "paren" ||
(token.type === "paren" && token.value !== ")")
) {
node.params.push(walk());
token = tokens[current];
}
current++;
return node;
}
throw new TypeError(token.type);
}
let ast = {
type: "Program",
body: [],
};
while (current < tokens.length) {
ast.body.push(walk());
}
return ast;
}
module.exports = parser;
Traverser
The traverser is a program that takes an AST and an object containing visitor methods, and traverses the AST recursively while calling the specified methods.
traverser.js:
function traverser(ast, visitor) {
// recursive function that will iterate through the AST and call the visitor methods
function traverseArray(array, parent) {
array.forEach((child) => {
traverseNode(child, parent);
});
}
// recursive function that will iterate through the AST and call the visitor methods
function traverseNode(node, parent) {
let methods = visitor[node.type];
if (methods && methods.enter) {
methods.enter(node, parent);
}
switch (node.type) {
case "Program":
traverseArray(node.body, node);
break;
case "CallExpression":
traverseArray(node.params, node);
break;
case "NumberLiteral":
case "StringLiteral":
break;
default:
throw new TypeError(node.type);
}
if (methods && methods.exit) {
methods.exit(node, parent);
}
}
// start traversing the AST
traverseNode(ast, null);
}
module.exports = traverser;
Transformer
The transformer is a program that takes an AST and returns a new AST.
transformer.js:
const traverser = require("./traverse");
function transformer(ast) {
let newAst = {
type: "Program",
body: [],
};
ast._context = newAst.body;
traverser(ast, {
NumberLiteral: {
enter(node, parent) {
parent._context.push({
type: "NumberLiteral",
value: node.value,
});
},
},
StringLiteral: {
enter(node, parent) {
parent._context.push({
type: "StringLiteral",
value: node.value,
});
},
},
CallExpression: {
enter(node, parent) {
let expression = {
type: "CallExpression",
callee: {
type: "Identifier",
name: node.name,
},
arguments: [],
};
node._context = expression.arguments;
if (parent.type !== "CallExpression") {
expression = {
type: "ExpressionStatement",
expression: expression,
};
}
parent._context.push(expression);
},
},
});
return newAst;
}
module.exports = transformer;
Code Generator
The code generator is a program that takes an AST and returns a string.
codegenerator.js:
function codeGenerator(node) {
switch (node.type) {
case "Program":
return node.body.map(codeGenerator).join("");
case "ExpressionStatement":
return codeGenerator(node.expression) + ";";
case "CallExpression":
return (
codeGenerator(node.callee) +
"(" +
node.arguments.map(codeGenerator).join(", ") +
")"
);
case "Identifier":
return node.name;
case "NumberLiteral":
return node.value;
case "StringLiteral":
return '"' + node.value + '"';
default:
throw new TypeError(node.type);
}
}
module.exports = codeGenerator;
Compiler
The compiler is a program that takes a string of JavaScript code as input and returns a string of JavaScript code as output.
compiler.js:
const codeGenerator = require("./codegenerator");
const lexer = require("./lexer");
const parser = require("./parser");
const transformer = require("./transformer");
function compiler(input) {
// tokenize the input
let tokens = tokenizer(input);
// parse the tokens
let ast = parser(tokens);
// transform the AST
let newAst = transformer(ast);
// generate the output
let output = codeGenerator(newAst);
return output;
}
module.exports = compiler;
Running the Compiler
const compiler = require("./compiler");
let input = "(add 2 (subtract 4 2))";
let output = compiler(input);
console.log(output);
The Result
add(2, subtract(4, 2));
Further Reading
Compiler Explorer
Writing a Compiler in Go
How to Write a Compiler
The Super Tiny Compiler